In the pursuit of sustainable living and energy conservation, the architectural industry has seen a significant rise in the adoption of innovative technologies. One such advancement is the use of Low-E (Low Emissivity) glass, a revolutionary building material that plays a pivotal role in making living spaces more energy-efficient. This article explores the benefits and features of Low-E glass and how it contributes to creating a more sustainable and comfortable environment.
Understanding Low-E Glass
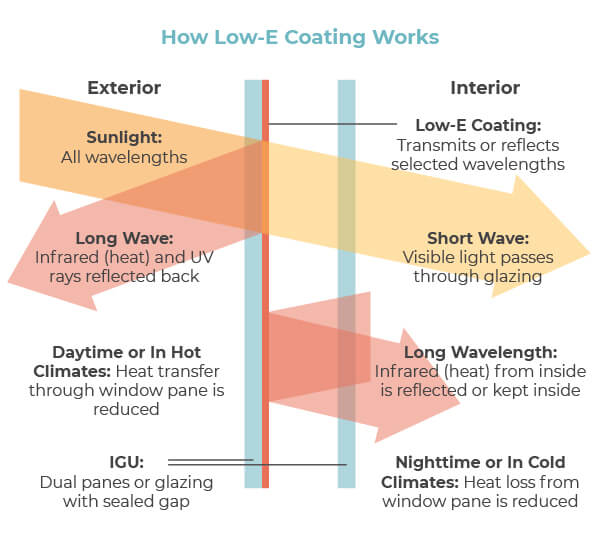
Low-E glass is coated with a thin, virtually invisible layer of metal or metallic oxide, which allows it to reflect infrared light while allowing visible light to pass through. This unique property helps in regulating the amount of heat that enters or leaves a building, making it a key player in energy-efficient architecture. The term “emissivity” refers to a material’s ability to emit radiant energy, and in the case of Low-E glass, it excels at minimizing heat transfer.
Energy Efficiency in Insulation
One of the primary benefits of Low-E glass is its ability to enhance insulation. Traditional windows, especially single-pane ones, are notorious for allowing heat to escape during the winter and allowing excessive heat to enter during the summer. Low-E glass acts as a barrier, reflecting heat back into the interior during colder months and preventing external heat from penetrating during warmer months. This results in reduced reliance on heating and cooling systems, leading to lower energy consumption and utility bills.
Read More:
UV Protection
Another noteworthy feature of Low-E glass is its capability to block harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. UV rays can cause fading and damage to furniture, flooring, and other interior elements. Low-E glass helps protect your belongings by minimizing the penetration of these rays, ensuring the longevity of your possessions and reducing the need for replacements or repairs.
Daylight Harvesting
Low-E glass strikes a balance between energy efficiency and natural daylighting. While it reflects infrared radiation, it allows visible light to pass through. This feature, known as “daylight harvesting,” enables residents to enjoy ample natural light without compromising on thermal comfort. The result is a well-lit and comfortable living space that minimizes the need for artificial lighting during the day.
Environmental Impact
By reducing the reliance on heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, Low-E glass contributes to lower carbon emissions. The decreased energy consumption not only benefits homeowners in terms of cost savings but also aligns with global efforts to combat climate change. Sustainable building practices, including the use of energy-efficient materials like Low-E glass, are essential for creating a greener and more environmentally friendly future.
Read More:
Learn More
As the world continues to prioritize sustainability, the adoption of technologies like Low-E glass becomes increasingly important in the journey towards a more eco-friendly and comfortable built environment.
Want more information on Low-E Glass? Techni-Glass can help! Get Started by sending your questions below!

